Packaging films play a pivotal role in safeguarding products across various industries, from food to pharmaceuticals and electronics. As an integral component of modern packaging solutions, these films offer protection, enhance shelf-life, and promote brand messaging through design and functionality. This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental aspects of packaging film, including definitions, types, industrial applications, its evolution, and future developments. Whether you're a manufacturer looking into thermoforming film suppliers or searching for lidding film food packaging solutions, understanding packaging film can greatly enhance your packaging strategy.
Basic Definition
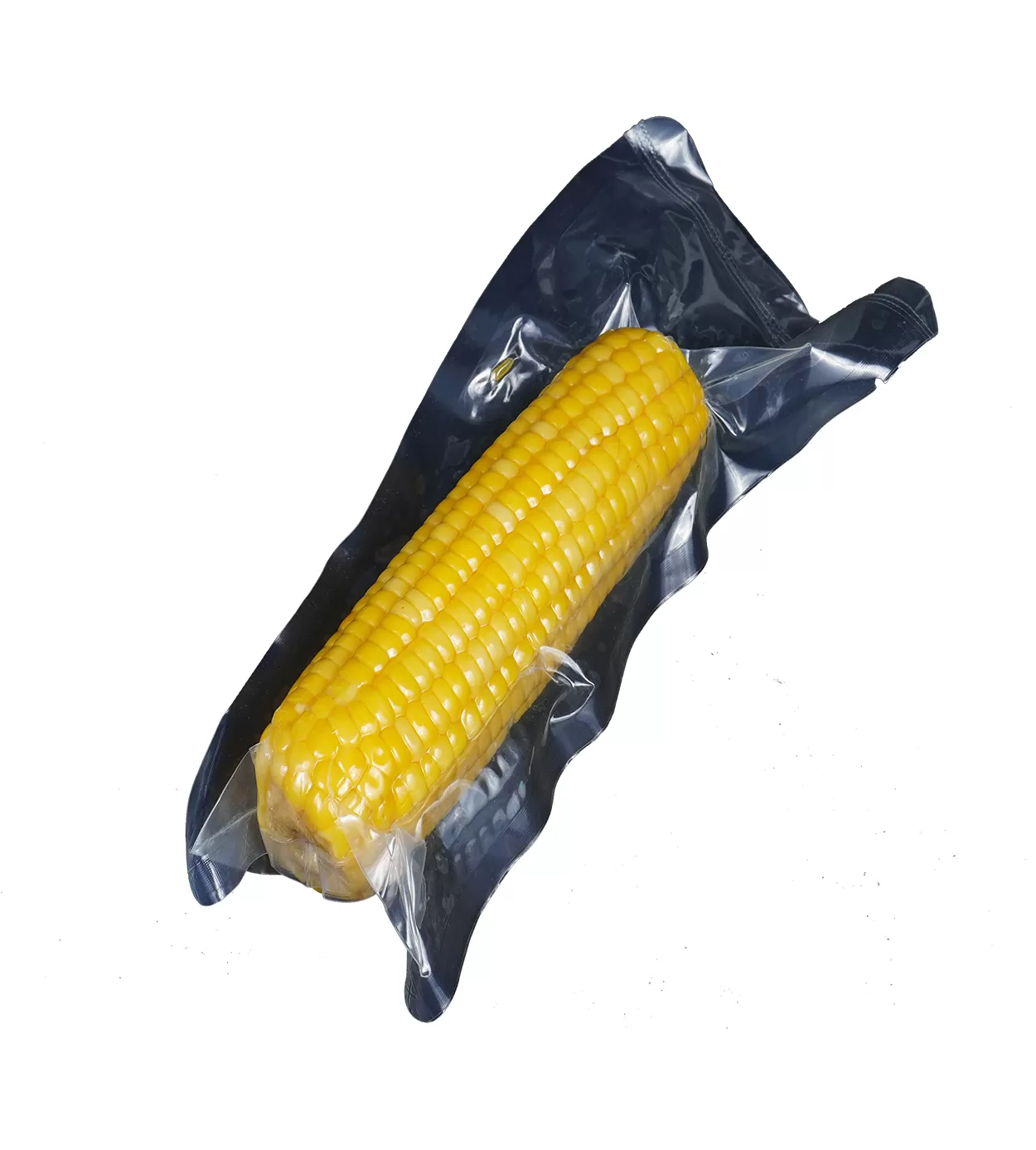
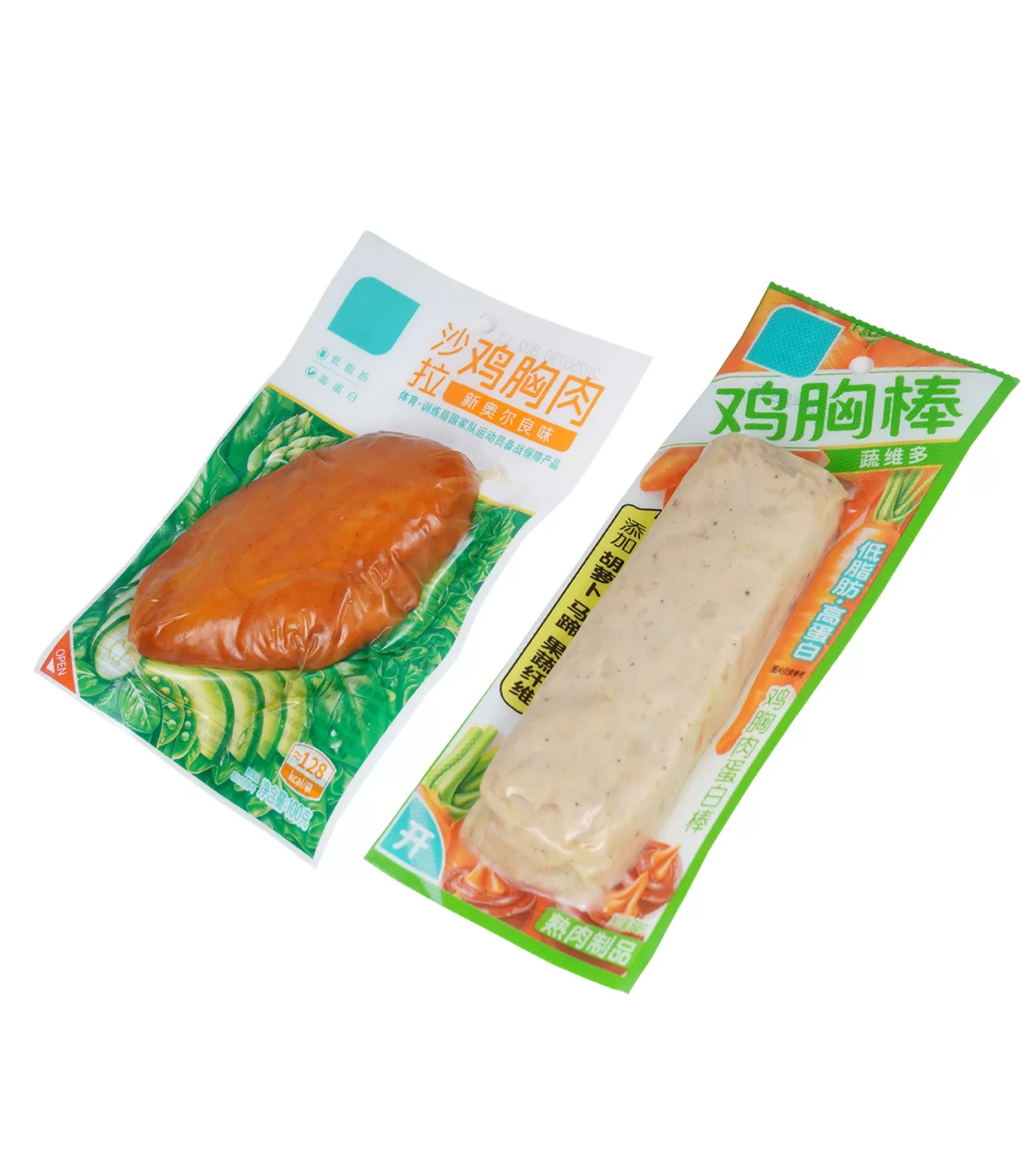
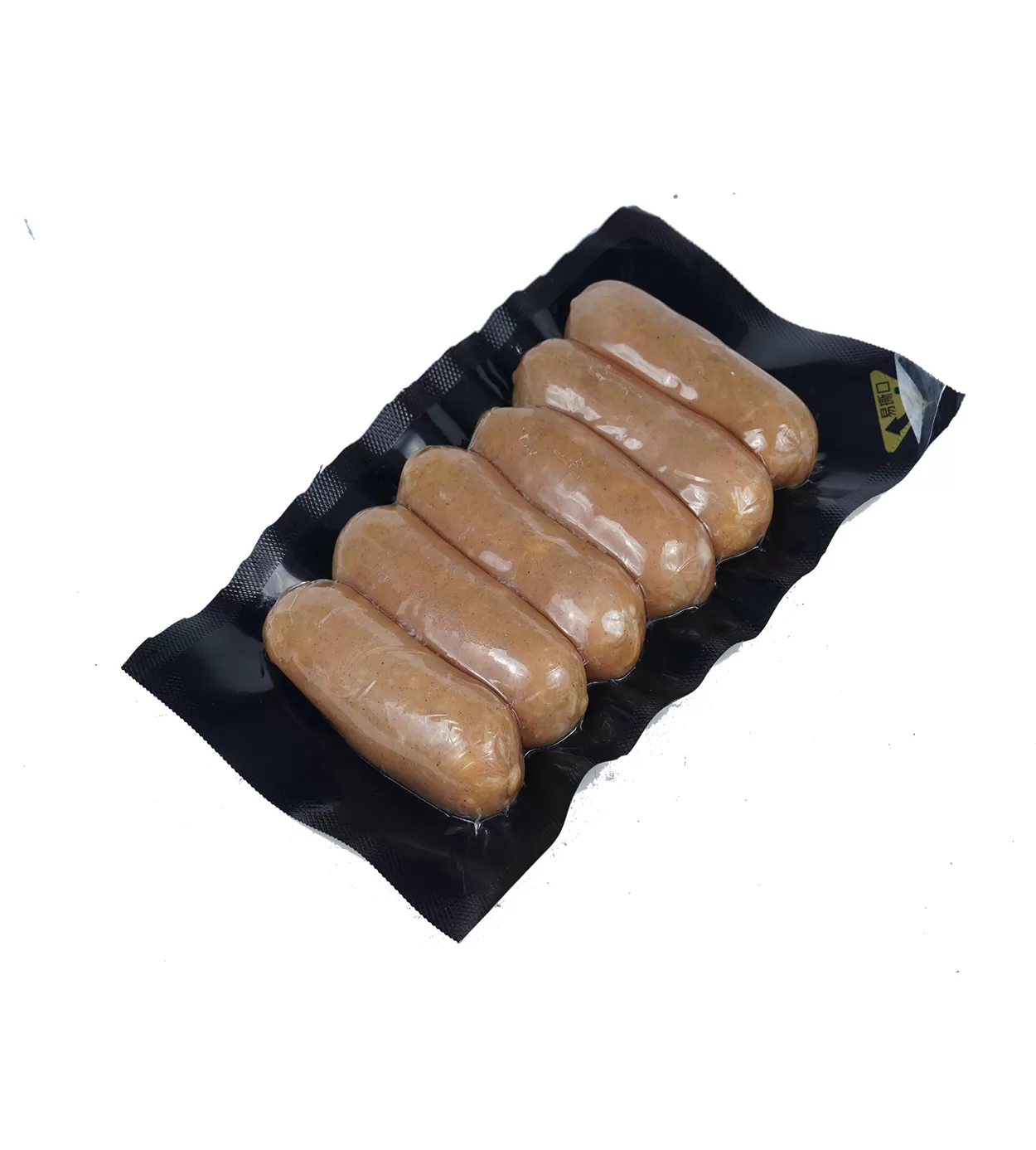
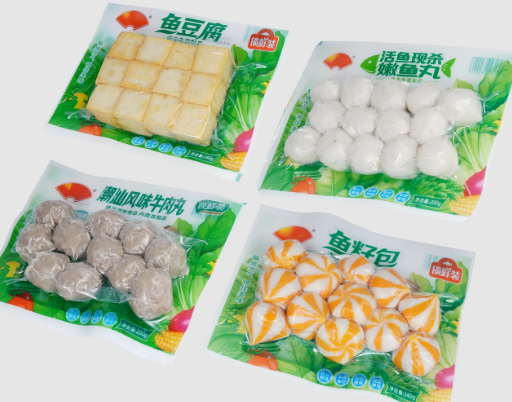
Packaging film refers to thin plastic sheeting that enwraps products for protection, preservation, and aesthetics. These films are formed from materials such as PE (polyethylene), PP (polypropylene), PA (Polyamide,Nylon) and EVOH (Ethylene-Vinyl Alcohol Copolymer), each providing unique characteristics suitable for different applications. Food packaging films are commonly used to protect perishable goods like meats and vegetables, ensuring they remain fresh and uncontaminated.
Material | Properties | Used as |
Polyethylene (PE) | Moisture barrier, Low-temperature heat sealing performance, Clarity | Outer layer, Contact layer, Sealing layer |
Polypropylene (PP) | Moisture barrier, High-temperature resistant retort, Clarity | Outer layer, Contact layer, Sealing layer |
Polyamide, Nylon (PA) | Puncture resistance, Excellent tensile strength | Inner layer, Outer layer, Protective layer, Support layer |
Ethylene-Vinyl Alcohol Copolymer (EVOH) | Flexible, Durable, Puncture resistance | Inner layer, Barrier layer (Extend the shelf life) |
Co-extrusion Cast Film | Uniform thickness, Excellent clarity, Puncture-resistant, High-barrier | Food Packaging, Medical Packaging, etc... |
Types and Varieties
Packaging films are not one-size-fits-all; they come in numerous varieties tailored to specific needs. MDO stretch films, used primarily in Lamination & printing,with enhanced stretchability, it minimizes film usage without compromising strength. Barrier films are utilized for extending product shelf-life by controlling oxygen transmission rates, while lidding films are applied to containers for a tamper-evident seal.
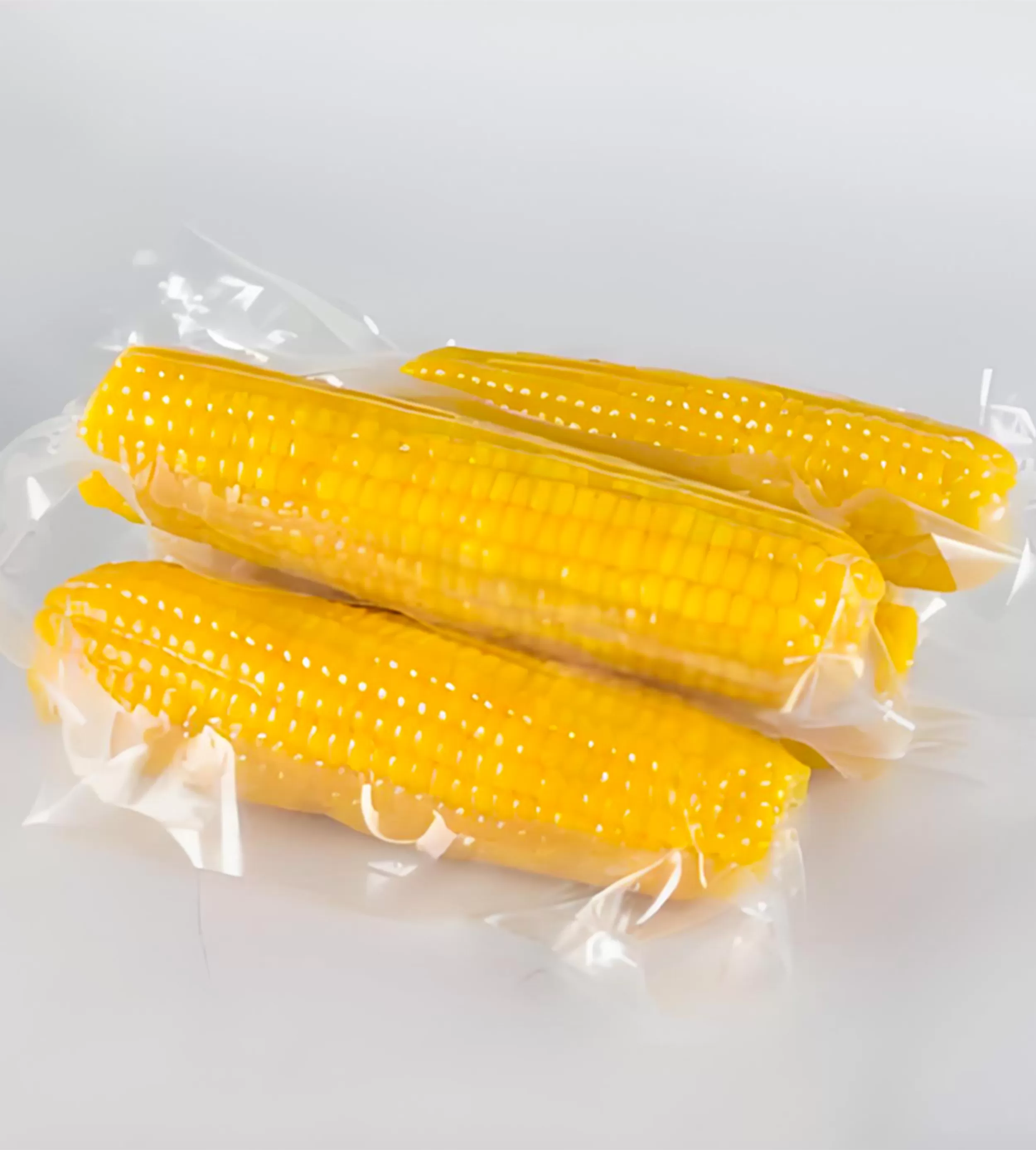
Additionally, packaging films are categorized into several types such as shrink films, often used to fit around products through heat application, and vacuum film packaging, crucial in preserving food products by removing air before sealing. Advances in technology have birthed eco-friendly food packaging film options that prioritize sustainability without compromising functionality.
Industrial Applications
The versatility of packaging films means they are suited for a vast range of industrial applications. In food sectors, films are used to maintain freshness, enhance appeal, and convey product information. The electronics industry relies on anti-static films to prevent damage from electrostatic discharge during transportation. Moreover, pharmaceuticals depend on barrier films to ensure product integrity against moisture and contaminants.
MAP packaging strategies often integrate various types of films to optimize protection and presentation. For example, combining vacuum pack rolls with lidding film food packaging provides an airtight, secure package that maintains product quality. Thus, understanding the specific application needs is crucial in selecting the right film type and supplier.
Evolution Over Time
From early waxed paper wraps to today's advanced multi-layer films, packaging technology has evolved to meet increasing demands for protection, convenience, and environmental friendliness. Innovations in materials science have paved the way for lighter, stronger, and more functional films that cater to dynamic market needs.
Past decades have seen enhancements in thermoforming film suppliers and lidding film development focusing on usability, cost efficiency, and sustainability. The shift toward healthier lifestyles has further propelled technology advancements in vacuum packaging bags for food to maximize edibility and quality preservation, proving essential to food safety.
Future Developments
The future of packaging films holds exciting prospects driven by digital technologies and heightened sustainability awareness. Anticipate innovations in smart films embedded with sensors to monitor product quality in real-time. The growing emphasis on the circular economy accentuates the importance of recyclable and biodegradable alternatives, encouraging cast film manufacturers to explore eco-friendly avenues.
Additionally, lidding film technology will continue advancing, with emphasis on high-performance sealing solutions that support both product integrity and consumer safety. As the packaging industry navigates these changes, businesses will need to align strategically with suppliers who support the transition to sustainable, high-tech solutions.
In conclusion, packaging films are a dynamic element of the industrial landscape, constantly adapting to meet demands for efficiency, safety, and sustainability. From vacuum pack freezer bags in food preservation to innovative seal mechanisms and material composition, their role in protection and presentation cannot be overstated. The ongoing advancements in this field highlight the need for businesses to stay informed and collaborate with leading packaging films experts to drive success in their operations. As we look to the future, sustainable innovation and smarter packaging promise a transformative impact on industries worldwide.
References:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/materials-science/polyethylene
https://www.plasticsindustry.org/polypropylene
https://www.packaging-gateway.com/news/film-packaging-developments/