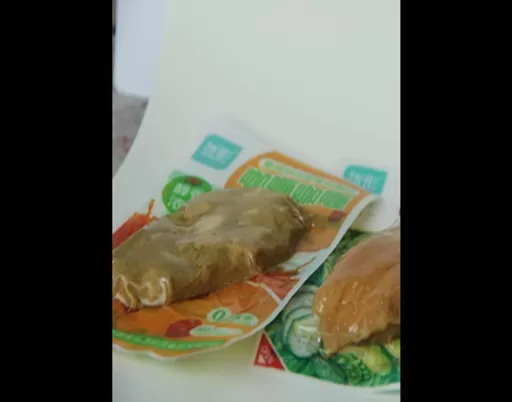
Thermoforming has become one of the most widely used packaging technologies across industries, especially for food, medical, and industrial products. Its ability to create custom-shaped packaging quickly, economically, and with excellent protective properties makes it indispensable in modern manufacturing.
About Thermoforming Packaging
Thermoforming packaging is a manufacturing process where a thermoplastic film is heated until pliable and then shaped over a mold using vacuum or pressure. Once cooled, the formed film retains the shape of the mold, creating custom cavities that securely cradle the packaged product.
There are two main types of thermoforming: vacuum forming, which uses suction to draw the heated film into the mold; and pressure forming, which uses air pressure to press the film into the mold for more detailed contours.
Thermoforming packaging is preferred for its design flexibility, fast production rates, and material efficiency. Unlike rigid molding methods, thermoforming uses thin plastic film, reducing material costs and waste.
Thermoforming Process Steps
1. Film Feeding and Heating
Thermoforming begins by unwinding a roll of thermoplastic film. The film is passed through an infrared or convection heater that softens it to the desired temperature. The heating zone and temperature profile are precisely controlled to ensure uniform material softness.
2. Forming into Mold
Once heated, the softened film is placed over or into a mold.
3. Cooling and Setting
After forming, the film cools rapidly, solidifying its shape. Cooling mechanisms integrated into molding tools help speed this step and maintain dimensional accuracy.
4. Trimming and Finishing
The formed film sheet is then trimmed to remove excess material and separate individual packaging units. Additional operations such as labeling, printing, or sealing with a lidding film can follow depending on product requirements.
Why Thermoforming Packaging Matters?
Thermoforming packaging has rapidly gained adoption across industries because it combines design freedom, efficiency, and protection.
Design Flexibility: Thermoforming can produce complex shapes, deep draws, and multiple cavities, ideal for packaging products with unique geometries.
Rapid Production and Scalability: Thermoforming machines can produce hundreds to thousands of packages per hour, making them suitable for both small and large-scale operations.
Cost-Effective Material Use: Compared with injection molding or blow molding, thermoforming consumes less plastic material and generates less waste.
Excellent Barrier and Protection: When using multilayer films, thermoforming packaging can protect products from moisture, oxygen, and contaminants, extending shelf life and maintaining quality. This is especially important for food and medical applications.
Common Material Options for Thermoforming Packaging
1. Polyethylene (PE)
Widely used due to its good formability and cost-effectiveness. Low-density (LDPE) and linear low-density (LLDPE) variants provide flexibility and toughness.
2. Polypropylene (PP)
Offers higher heat resistance and rigidity compared to PE. It’s ideal for packaging requiring a clean presentation and strength.
3. Ethylene-Vinyl Alcohol Copolymer (EVOH)
It is a high-performance material known for its excellent barrier properties against gases (like oxygen and carbon dioxide), moisture, and aromas, making it widely used in packaging applications.
4. Multilayer Coextruded Films
These films combine different polymers to balance barrier performance, formability, seal integrity, and mechanical strength. Barrier layers such as EVOH are integrated to significantly reduce oxygen and moisture transmission, essential for food and medical packaging.
GroupSmart GSFORM Series: High-Performance Thermoforming Packaging Materials
When material selection matters for quality and performance, the GSFORM Series Thermoforming Packaging Materials offer a strong solution for both standard and demanding packaging applications, ideal for advanced packaging demands in food, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and industrial goods. These films offer high-quality, customizable solutions to fit diverse production needs and deliver consistent, high performance.
Multilayer Barrier Structures: Designed for superior oxygen and moisture resistance.
Excellent Formability: Optimized for deep draws and high-speed thermoforming lines.
Consistent Thickness and Uniformity: High quality standards for reliable sealing and performance.
Customizable Specifications: Available in various thicknesses, barrier levels, and film structures to match specific application requirements.
Applications of Thermoforming Packaging
Thermoforming packaging is widely adopted in diverse industries due to its adaptability and performance.
Food Packaging
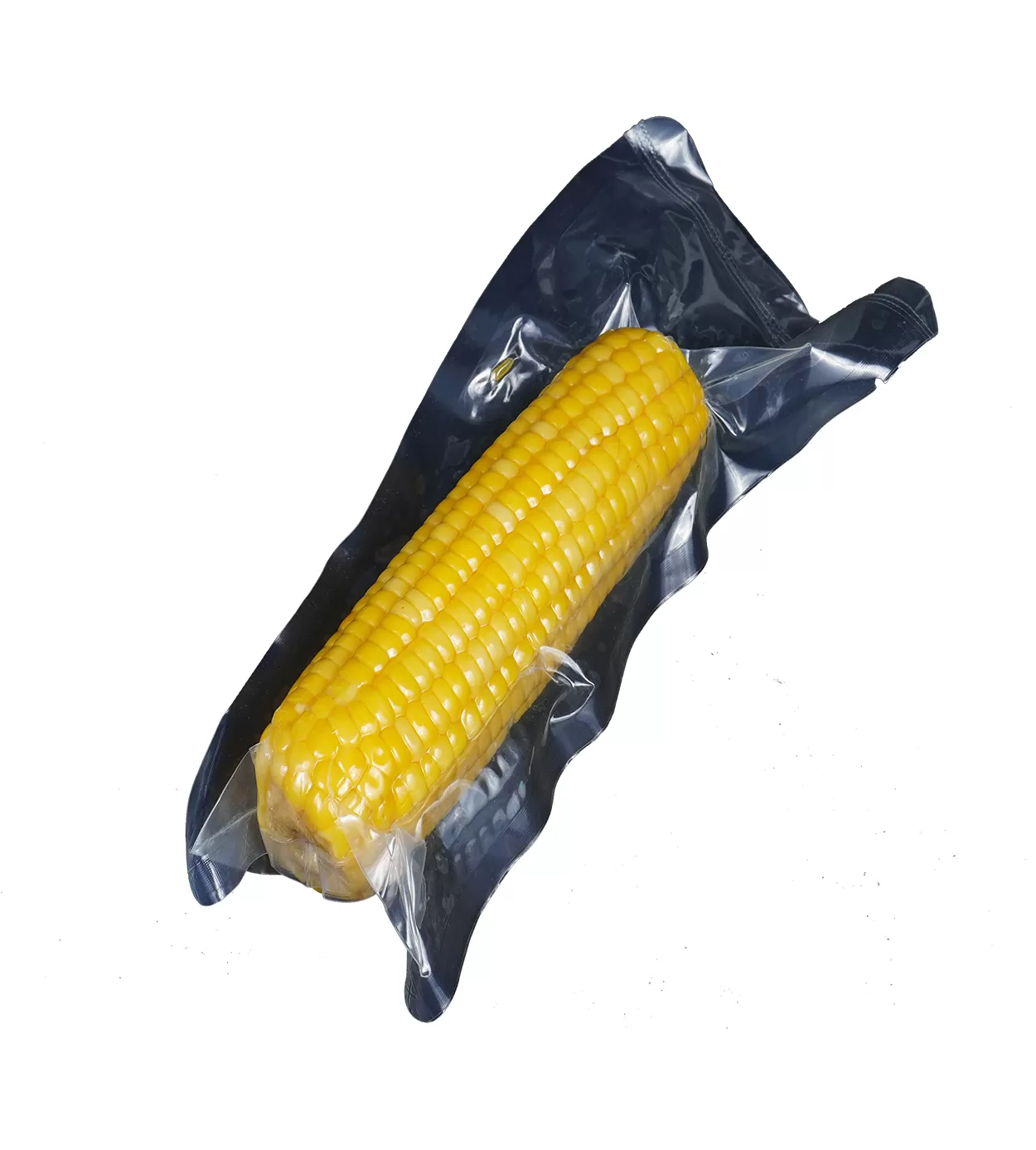
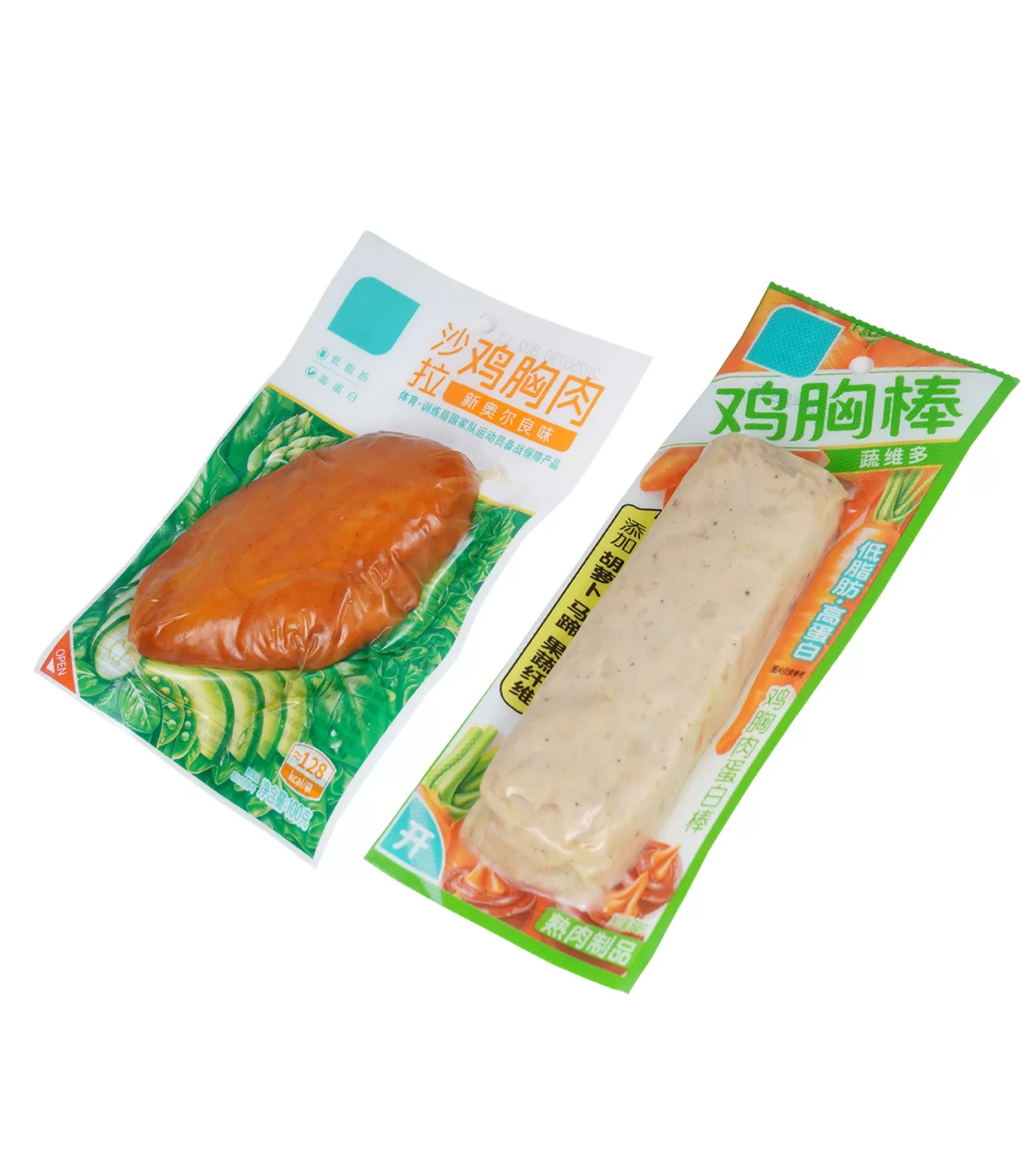
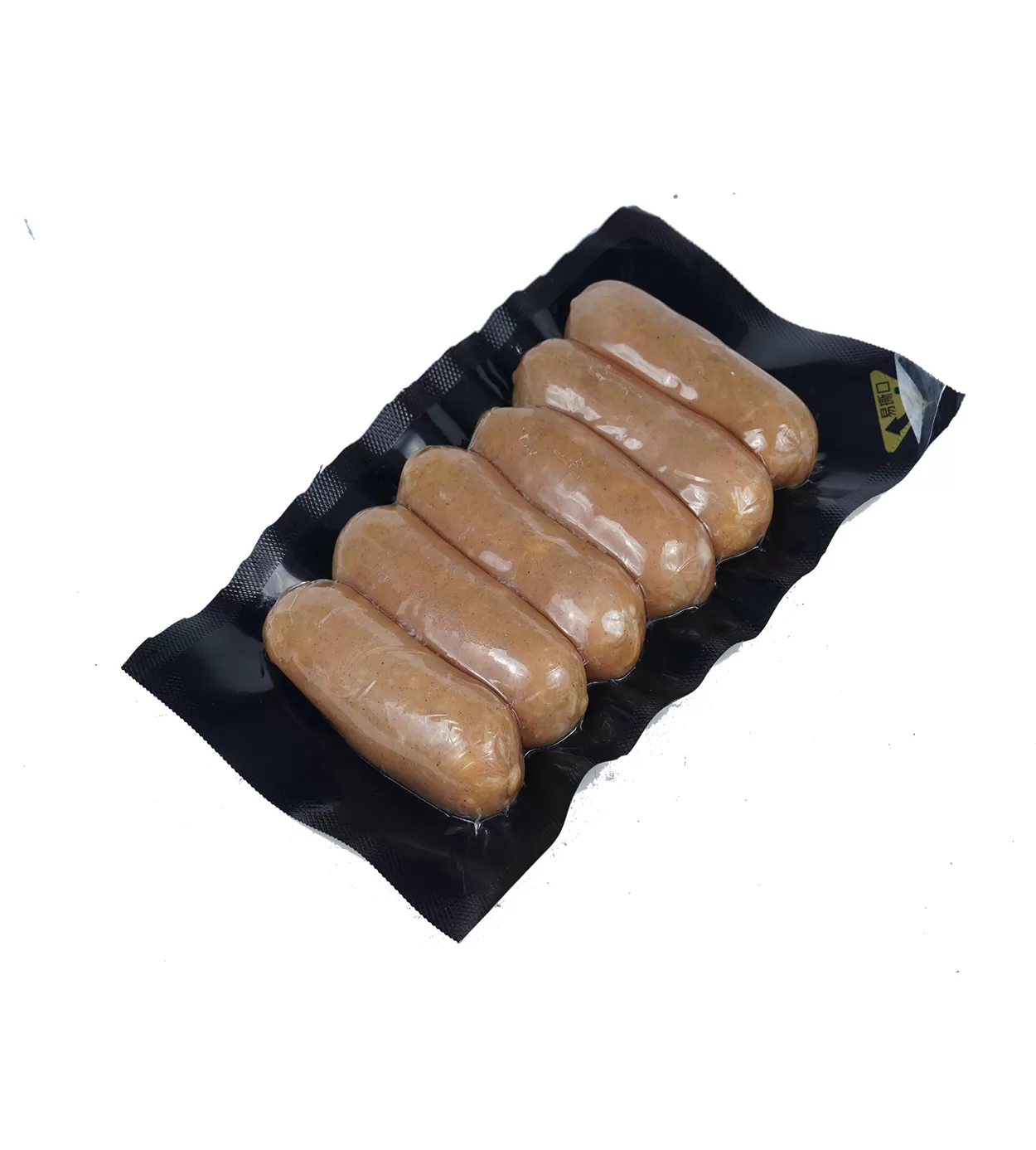
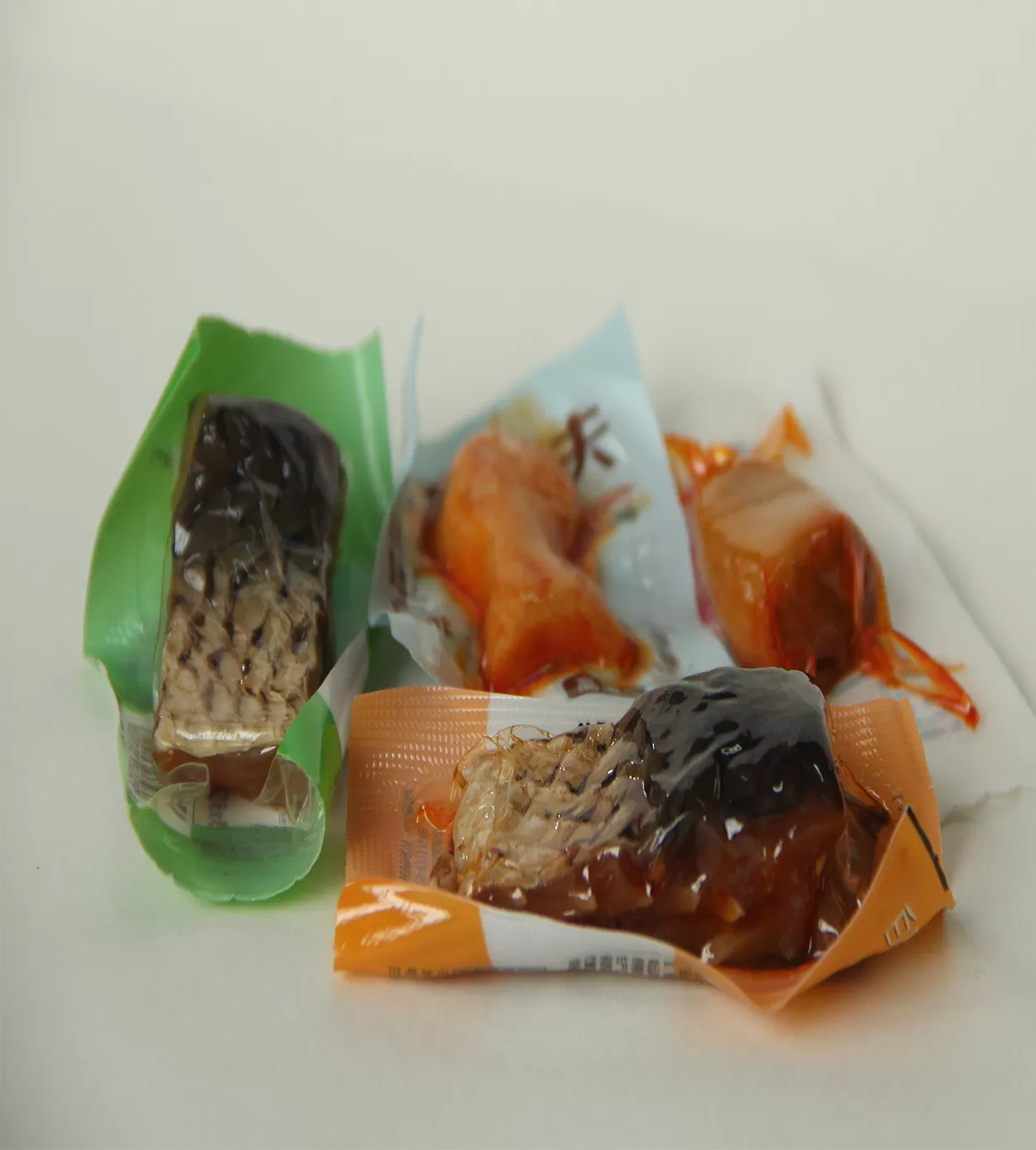
In food packaging, thermoforming film is used to produce trays, vacuum packages, and protective enclosures for fresh meat, fish, poultry, deli, and delicatessen products. The deep draws and barrier performance maintain product quality and extend shelf life.
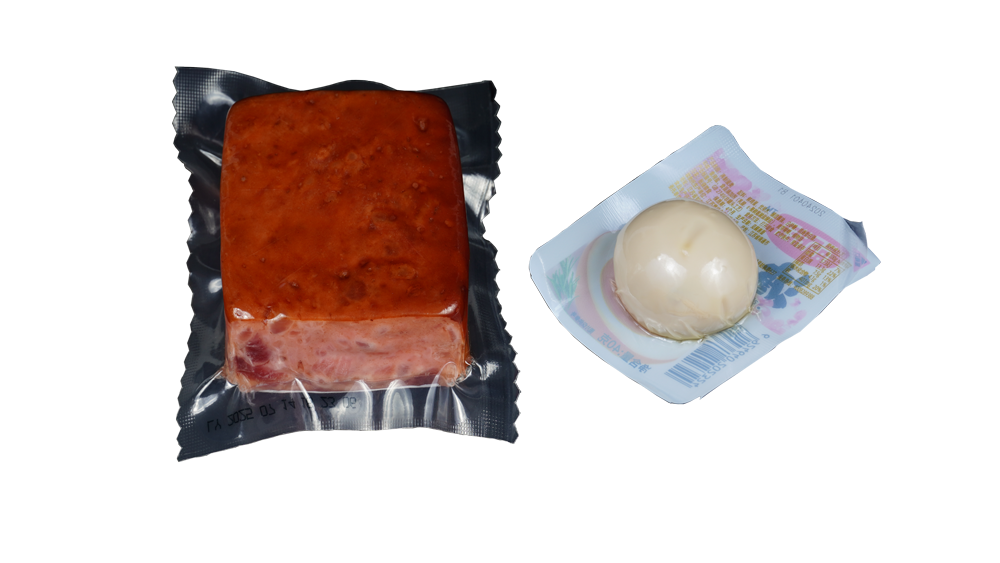

Medical and Pharmaceutical Packaging
Thermoforming packaging is ideal for sterile medical devices, pharmaceutical blister packs, and diagnostic tools. Its excellent barrier properties protect sensitive products from moisture, oxidation, and contamination. Custom packaging film structures allow precise control over performance.
Consumer and Industrial Products
From electronic components to hardware parts, thermoforming packaging offers excellent mechanical protection, corrosion resistance, and tailored cavity design for safe transport and storage. Its ability to produce precise, repeatable shapes makes it cost-effective for high-volume runs.
Thermoforming Packaging Design Considerations
1. Product Protection Requirements
Understand the sensitivity of the product to moisture, oxygen, or light. Pharmaceuticals and perishable foods often require high barrier materials.
2. Formability and Material Behavior
Some materials form better in deep draws, while others provide enhanced barrier characteristics. Understanding the processing window of each material is key.
3. Packaging Line Compatibility
Ensure the material is compatible with existing thermoforming lines, including temperature ranges, forming depth, and sealing conditions.
4. Sustainability Objectives
Recyclability, material efficiency, and waste reduction should be part of the material selection process.
Thermoforming packaging continues to evolve in response to changing market demands and technological advancements. One of the most significant trends is the ongoing enhancement of barrier performance, which allows packaging to better protect products from oxygen, moisture, and other external factors, thereby extending shelf life and maintaining product quality.
In addition, smarter packaging design is playing a critical role in reducing overall material consumption without compromising strength or functionality. Optimized film structures and improved forming efficiency help minimize waste while maintaining reliable performance. Alongside these material innovations, greater automation and inline quality control are being integrated into thermoforming production lines. These advancements improve consistency, increase output, and enable manufacturers to meet high-volume demands with greater precision, ultimately driving more sustainable and high-performance thermoforming packaging solutions.
Thermoforming packaging provides an efficient, versatile, and protective solution for a wide range of applications, from food to medical devices, consumer goods to industrial parts. Its combination of design flexibility, material efficiency, and barrier performance makes it a preferred choice for modern packaging.